Recognizing the Secret Differences In Between Kidney Stones and Urinary System System Infections: A Comprehensive Introduction for Patients
Recognizing the distinctions in between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is essential for people that might be experiencing similar signs and symptoms yet face significantly various health challenges. While both conditions can show up discomfort in the lower abdomen or back, their hidden reasons, diagnostic techniques, and treatment protocols diverge dramatically. A nuanced comprehension of these differences not just help in exact self-assessment but likewise informs discussions with doctor. As we discover these important aspects, it becomes clear that acknowledging the one-of-a-kind characteristics of each problem can exceptionally impact patient results. What might be the most effective method to resolving these differences?
Overview of Kidney Stones
The development of kidney stones, a usually devastating and excruciating condition, underscores the crucial value of maintaining kidney health and wellness. The main types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with unique reasons and threat factors.
A number of aspects contribute to the development of kidney stones. Furthermore, metabolic problems and specific clinical conditions might incline people to stone formation.
Signs and symptoms of kidney stones can include serious flank discomfort, nausea, and hematuria, which commonly trigger urgent clinical assessment. Treatment choices differ, ranging from enhanced liquid intake and nutritional modifications to clinical interventions such as lithotripsy or surgical elimination, depending on the dimension and location of the stones. Comprehending these elements is vital for effective prevention and management.
Review of Urinary System Infections
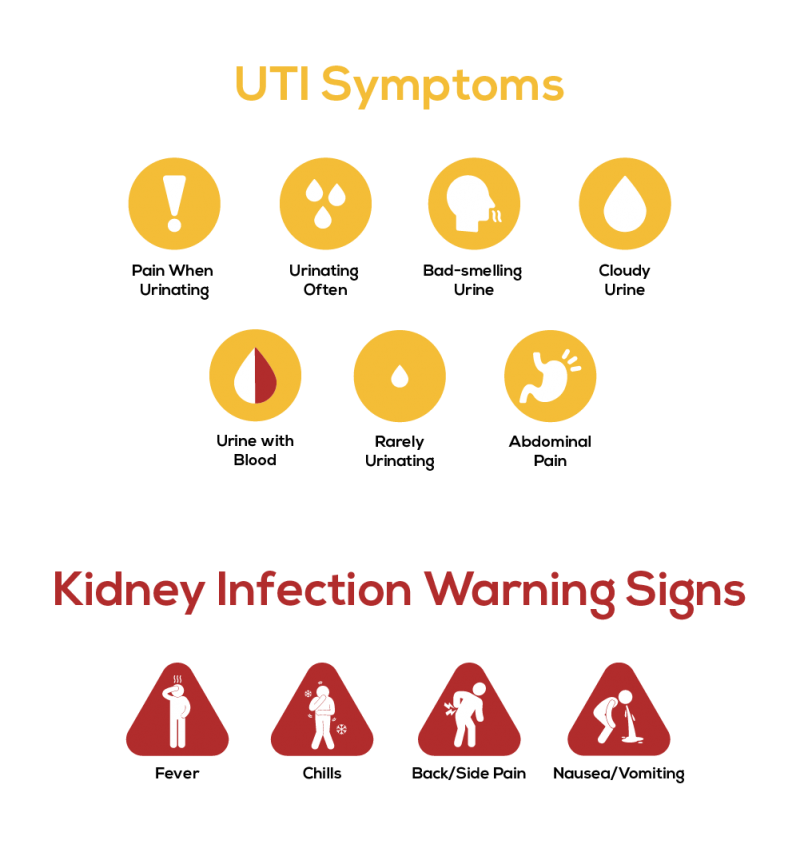
Urinary system system infections (UTIs) stand for an usual yet significant health and wellness issue, affecting millions of people yearly. These infections take place when microorganisms enter the urinary system, that includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The bulk of UTIs are triggered by Escherichia coli, a sort of germs typically located in the intestinal system. While UTIs can affect anyone, they are specifically prevalent in ladies as a result of physiological differences that promote bacterial entry.
The threat elements for establishing a UTI include sexual activity, certain types of birth control, urinary retention, and a history of previous infections. Uncomplicated UTIs are typically limited to the bladder and are much more common in healthy individuals, while complex UTIs may include the kidneys and happen in those with underlying health and wellness concerns.
Motivate medical diagnosis and therapy are crucial to prevent issues, such as reoccurring infections or kidney damage (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Typically, UTIs are treated with prescription antibiotics, and precautionary steps can be used for those with constant incidents
Typical Symptoms Comparison
Signs and symptoms of urinary system infections and kidney stones can often overlap, leading to complication in diagnosis. In contrast, kidney stones often tend to create serious, sharp discomfort that emits from the back to the lower abdominal area and groin, typically described as colicky pain.
In addition, UTIs might be accompanied by fever and cools, particularly in a lot more severe instances, while kidney stones can result in nausea and throwing up due to extreme discomfort. Both conditions can cause blood in the urine (hematuria), yet the presence of blood is a lot more commonly related to kidney stones. While pain during urination is a characteristic of UTIs, kidney stones normally present with even more sharp Check This Out pain episodes, which might go and come. Comprehending these sign differences can assist individuals in identifying their condition, although medical evaluation continues to be vital for exact medical diagnosis and therapy.
Diagnosis Techniques
Just how can medical care specialists accurately distinguish between kidney stones and urinary tract infections? The analysis procedure starts with a comprehensive case history and a thorough review of the person's signs and symptoms. Medical professionals commonly carry out a physical examination, which might disclose inflammation in the abdomen or flank region, guiding the diagnostic path.
Research laboratory examinations play a critical duty in comparing these two problems. Kidney Stones vs UTI. A urinalysis can recognize the presence of blood, crystals, or microorganisms, which are indicative of either problem. In instances of urinary tract infections, the urinalysis might reveal a significant presence of leukocyte and nitrites, while kidney stones may offer with details crystals
Imaging researches, such as stomach ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scans, are essential for visualizing kidney stones. These imaging techniques make it possible for doctor to examine stone size, location, and possible obstructions in the urinary system tract. On the other hand, urinary system tract infections generally do not call for imaging unless issues are thought.
Together, these analysis techniques empower health care professionals to properly identify and separate between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections, guaranteeing that people get ideal care and monitoring.
Treatment Options and Prevention
While both kidney stones and urinary tract infections (UTIs) call for prompt therapy, their administration strategies differ dramatically.
The treatment for kidney stones often involves pain administration, hydration, and sometimes, clinical procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or ureteroscopy to damage or remove down stones. Clients are regularly advised to increase fluid consumption to promote stone passage and decrease recurrence. Dietary modifications may likewise be required, depending on the stone type.
On the other hand, UTIs are primarily treated with prescription antibiotics to remove the bacterial infection. The particular antibiotic prescribed depends on the germs determined and local resistance patterns. Extra procedures, such as increased liquid intake and urinary analgesics, may assist ease signs.
Prevention techniques differ too; for kidney stones, maintaining sufficient hydration and sticking to nutritional constraints can be efficient. For UTIs, preventive approaches include proper health methods, urinating after intercourse, and possibly prophylactic antibiotics for reoccurring infections. Comprehending these therapy and avoidance modalities is necessary for efficient administration and to lessen the risk of complications linked with both conditions.
Conclusion
_1668065966.png)
Recognizing the differences in between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is important for people that may be experiencing similar symptoms yet encounter greatly different wellness obstacles. The primary kinds of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with distinctive reasons and threat variables.